Share This

Pages on this site may contain affiliate links, meaning if you book or buy something, I may earn an affiliate commission at no additional cost to you. Thank you for your support! Learn More
Also note: While I am a certified nutrition coach, I am not a medical doctor. Information here is not intended to be a replacement for the advice you should seek from your doctor.
High Level Benefits of Kombucha
The health benefits of kombucha are inherited from the benefits of all fermented foods and drinks. At a basic level, kombucha contains live microbes (AKA “good” bacteria) in your microbiome that combat pathogenic (“bad”) ones, strengthening biological processes. Read on for the numerous other benefits drinking kombucha can provide.
Essential Definitions
Microbiome – the microorganisms in a particular environment (including the body or a part of the body)
Microbe – a microorganism, especially a bacterium causing disease or fermentation
Gut flora – the symbiotic bacteria occurring naturally in the intestine.
Kombucha contains live microbes that combat pathogenic (“bad”) ones.
Fermented foods and drinks contain live microbes that combat pathogenic microbes. These microbes are similar to those that make up a healthy gut microbiome, thus facilitating a favorable gut flora balance. The “good” microbes do this by:
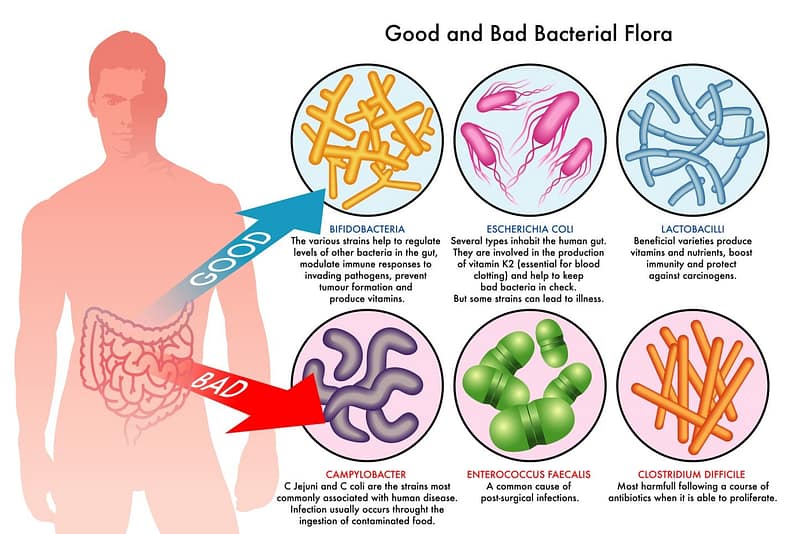

- Joining and interacting with other microbes in our bodies thus strengthening biological processes such as digestion and immune function.
- Maintaining or restoring the lining of our gut, thus improving body’s resistance to bad microbes and inorganic toxins (such as heavy metals), as well as partially digested proteins which can provoke undesirable immune responses.
Unfiltered kombucha contains yeast which is full of vitamins, minerals, enzymes and antioxidants
Note, I said “unfiltered”. Store bought kombucha is more often than not filtered and pasteurized. If you are buying kombucha, try to find “raw” on the label. In an attempt to kill any potential “bad” bacteria, the pasteurization process also kills the “good” bacteria (2). “Raw” brands should be unfiltered as well which means all the beneficial yeast is still present. The only way you can really know how the kombucha was made, is to make it yourself! The following can be found in unfiltered kombucha (1):
- Vitamins – including vitamin C and B vitamins B1, B6 and B12.
- Small amounts of protein
- Trace minerals such as selenium and chromium
- Enzymes – helps break down food for digestion
- Antioxidants – polyphenols, flavonoids, resveratrol, etc.
Kombucha is acidic and slightly alcoholic keeping pathogenic microbes under control
Acidic and alcoholic environments limit the ability of other organisms, such as possible contaminants, to grow. The slightly acidic and alcoholic nature of kombucha in small doses isn’t harmful, and can keep pathogenic microbes under control (3).


❤️❤️ Don’t miss a recipe or post! Make sure you remember to sign up for my Newsletter and follow me on social ❤️❤️!
Get Your Free Stuff!
The fermentation of kombucha can increase bioavailability of nutrients that occur naturally in foods
Bioavailability is the percentage of nutrients in your food and drinks that can be processed by your body and can be used functionally. “Fermentation can help to ‘unlock’ the nutrients of these foods, causing important cellular changes to occur and allowing your body to better absorb and use the nutrients” (4).
One example of a compound that is broken down during fermentation is phytic acid, which normally binds to some minerals preventing our bodies from using them (1). The result of the phytic acid being broke down is more minerals being absorbed by the body.
More Granular Potential Benefits of Drinking Kombucha
With a favorable gut flora balance, the potential for your body to combat different diseases and other health issues increases. This favorable balance facilitates you being an all around healthier person. 😄
To read about the more granular potential benefits, such as for mental health and weight loss, read my article How Kombucha Can Benefit with Health Issues!
Please sign up for my email list to receive the new related articles in this Kombucha series as well as new recipes.
You have little control over the brewing process and cost when you buy it from the store. Try brewing it at home instead!
1. Guajardo, Alex Lewin & Raquel. Kombucha, Kefir, and Beyond. s.l. : Quarto Publishing Group, 2017.
2. Pasteurized vs. Organic Raw Kombucha. Organic Brew Dr Kombucha. [Online] Dec 3, 2019.
3. C. J. GREENWALT, * K. H. STEINKRAUS, AND R. A. LEDFORD. ombucha, the Fermented Tea: Microbiology, Composition, and Claimed Health Effects. Journal of Food Protection. [Online] Feb 2000.
4. Ramba, Meredith. How Fermentation Can “Unlock” Your Foods’ Full Nutrient Potential. Edible Alchemy. [Online] Dec 9, 2018.













